蜘蛛丝蛋白助力疫苗激活免疫细胞
来源:《生物材料》
作者:Carole Bourquin等
时间:2018-07-03
瑞士和德国研究人员设计出一种制造疫苗的新方案:用蜘蛛丝蛋白把抗原包裹起来,能将抗原安全运送给淋巴组织中的T细胞,大幅增强疫苗激发免疫反应的效果。
瑞士日内瓦大学发布新闻公报说,该技术由该校与德国AMSILK公司合作开发,有助于设计稳定、易用、耐储存的疫苗。
对于癌症和一些重要传染病,需要把小块蛋白质碎片——抗原肽运送给T细胞,使其学会识别相关病原体,产生免疫力。如果直接注射,抗原肽在到达“目的地”之前就会分解,如何安全有效地运送抗原肽,是开发疫苗的一个难点。
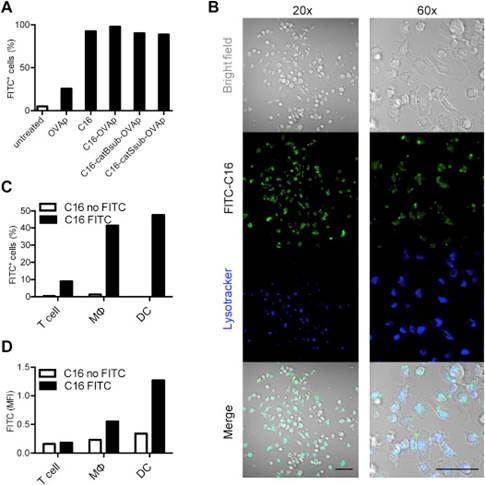
研究人员在国际期刊《Biomaterials》杂志上发表论文说,他们把抗原肽与一种蜘蛛丝蛋白相结合,制造出纳米尺寸的粒子,不需要疫苗佐剂就成功将抗原肽运抵并激活T细胞,且没有出现免疫毒性迹象。
这种疫苗粒子非常稳定,容易制造,可按需调整。此外,疫苗粒子的耐热性好,能在超过100摄氏度的环境中完好保存数小时。
研究人员说,如能在此技术基础上制造出不需要佐剂和冷链运输的疫苗,对提高发展中国家免疫接种率有重要意义。该技术理论上适用于所有的小分子抗原肽,但许多常规疫苗使用的抗原分子比较大,能否用这种新技术还需要进一步研究验证。 (来源:新华网)
Engineered hybrid spider silk particles as delivery system for peptide vaccines
Abstract The generation of strong T-cell immunity is one of the main challenges for the development of successful vaccines against cancer and major infectious diseases. Here we have engineered spider silk particles as delivery system for a peptide-based vaccination that leads to effective priming of cytotoxic T-cells. The recombinant spider silk protein eADF4(C16) was fused to the antigenic peptide from ovalbumin, either without linker or with a cathepsin cleavable peptide linker. Particles prepared from the hybrid proteins were taken up by dendritic cells, which are essential for T-cell priming, and successfully activated cytotoxic T-cells, without signs of immunotoxicity or unspecific immunostimulatory activity. Upon subcutaneous injection in mice, the particles were taken up by dendritic cells and accumulated in the lymph nodes, where immune responses are generated. Particles from hybrid proteins containing a cathepsin-cleavable linker induced a strong antigen-specific proliferation of cytotoxic T-cells in vivo, even in the absence of a vaccine adjuvant. We thus demonstrate the efficacy of a new vaccine strategy using a protein-based all-in-one vaccination system, where spider silk particles serve as carriers with an incorporated peptide antigen. Our study further suggests that engineered spider silk-based vaccines are extremely stable, easy to manufacture, and readily customizable.
原文链接:https://reader.elsevier.com/reader/sd/57FE19F5C7DE9E28031EE47F1ACC64EECCA6798E1ED313ED688EC90F49C8566F6E5C6766FF0456B1360CEED2E1417F5C




