首个藜麦高质量参照基因组公布
来源:《Nature》
作者:David E. Jarvis等
时间:2017-03-08
英国《自然》杂志8日在线发表的一篇植物科学论文,公布了首个藜麦高质量参照基因组。这项新成果将促进藜麦的遗传改良和育种策略,有望提高全球粮食安全。
藜麦是一种营养丰富、无麸质、血糖指数低的作物,所含人体必需的氨基酸、纤维、脂肪、碳水化合物、维生素能和矿物质达到出色的平衡,是唯一一种单体植物,可基本满足人体基本营养需求的食物。最重要的是,它能够在各种环境条件下生长。
这种植物其实已经有5000年至7000多年的食用和种植历史,在上世纪80年代,藜麦就被美国国家航空航天局用作宇航员太空食物。但迄今为止,藜麦仍属于一种利用不足的作物,为了扩大其在全球范围内的生产,还需要通过育种工作改善其农业性状。
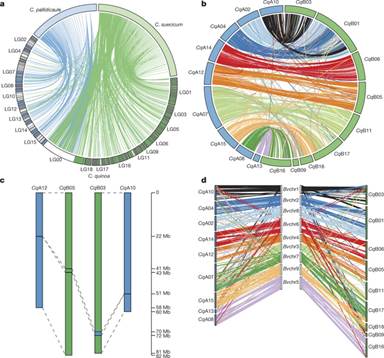
此次,沙特阿拉伯阿卜杜拉国王科技大学研究人员马克·泰斯特及其同事,检测了智利沿海的藜麦品种基因组序列以及另外的藜属品种基因组序列,以表征藜麦的遗传多样性,理解藜麦基因组的演化。
研究团队在进一步分析中,描述了其基因组数据以识别调控皂素形成的基因,皂素是藜麦籽壳中存在的一种苦味分子,必须在人类吸收之前去除。论文作者认为,他们发现的基因标记将可用于开发皂素含量低的无苦味或甜味藜麦商业品种。
在论文随附的新闻与观点文章中,美国佐治亚大学安德鲁·皮特森总结表示,该发现为加速藜麦的遗传改良打下基础,而其目标正是保障全球日益增多的人口的粮食安全。(来源:科技日报 记者张梦然)
The genome of Chenopodium quinoa
Abstract Chenopodium quinoa (quinoa) is a highly nutritious grain identified as an important crop to improve world food security. Unfortunately, few resources are available to facilitate its genetic improvement. Here we report the assembly of a high-quality, chromosome-scale reference genome sequence for quinoa, which was produced using single-molecule real-time sequencing in combination with optical, chromosome-contact and genetic maps. We also report the sequencing of two diploids from the ancestral gene pools of quinoa, which enables the identification of sub-genomes in quinoa, and reduced-coverage genome sequences for 22 other samples of the allotetraploid goosefoot complex. The genome sequence facilitated the identification of the transcription factor likely to control the production of anti-nutritional triterpenoid saponins found in quinoa seeds, including a mutation that appears to cause alternative splicing and a premature stop codon in sweet quinoa strains. These genomic resources are an important first step towards the genetic improvement of quinoa.
原文链接:http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nature21370.html




