植物基因组编辑突变体筛选方法研究取得进展
来源:《植物生物技术杂志》
作者:梁振等
时间:2018-06-19
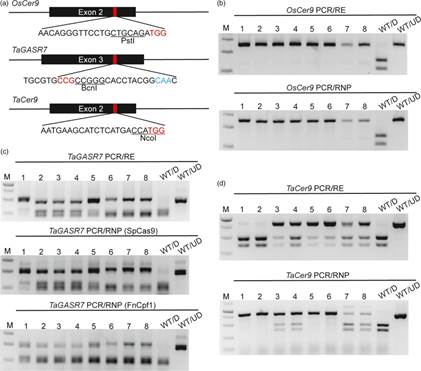
如何快速高效进行突变体检测和鉴定是植物基因组编辑技术迅速发展面临的重要问题之一。目前植物基因组编辑突变检测方法主要包括 PCR/RE、T7EI 错配切割、临界退火温度 PCR (ACT-PCR)、Sanger 测序和二代测序 (NGS) 等。以上所有的检测方法都基于 PCR 反应,且都有各自的不足之处。PCR/RE 方法的需要设计含有限制性内切酶位点的靶位点;T7EI 无法区分纯合突变体和野生型以及杂合突变体与双等位突变体;ACT-PCR 对 PCR 反应条件要求极高,而且无法检测到杂合突变;Sanger 测序和 NGS 的价格比较昂贵,尤其是对于数目比较大的群体。
针对上述问题,中国科学院遗传与发育生物学研究所高彩霞研究组利用 CRISPR/Cas 系统 (包括 Cas9 和 Cpf1) 的体外切割特性,在六倍体小麦和二倍体水稻中建立了一种简单、高效、廉价的 PCR/RNP 植物突变体筛选策略。该方法不受限制性内切酶位点的限制,比 PCR/RE 具有更强的广适性;比 T7EI 具有更高的准确度;比 Sanger 测序更廉价,而且灵敏度更高。基于 SpCas9 和 FnCpf1 RNPs 的 PCR/RNP 方法可以用于检测基因组编辑中经 NHEJ 修复产生的所有 indel 突变;基于 FnCpf1 RNPs 的 PCR/RNP 方法可以用于检测位于种子区域 (seed region) 内的 SNP 突变。该方法尤其适用于小麦的瞬时表达基因组编辑体系,如该实验室之前建立的 CRISPR/Cas9 IVTs 和 RNPs 介导的 DNA-free 基因组编辑体系。这是由于瞬时表达基因组编辑体系在后续组织培养过程中不使用任何的筛选标记,在 T0 代会获得较多的待筛选植株,而且 PCR/RNP 方法可以使用通用引物对发生在小麦 A 组、B 组和 D 组各拷贝的突变进行同时检测,不会受靶位点周围 SNPs 的影响。此外,PCR/RNP 方法也可以用于检测 TALEN 蛋白所诱导的突变。
该研究成果于 5 月 3 日在线发表于 Plant Biotechnology Journal 杂志上(DOI: 10.1111/pbi.12938)。高彩霞研究组博士生梁振为该论文的第一作者。相关研究得到科技部、北京市科委、中科院以及国家自然基金委的资助。(来源:中国科学院遗传与发育生物学研究所)
Genotyping genome‐edited mutations in plants using CRISPR ribonucleoprotein complexes
Abstract Despite the great achievements in genome editing, accurately detecting mutations induced by sequence‐specific nucleases is still a challenge in plants, especially in polyploidy plants. An efficient detection method is particularly vital when the mutation frequency is low or when a large population needs to be screened. Here, we applied purified CRISPR ribonucleoprotein complexes to cleave PCR products for genome‐edited mutation detection in hexaploid wheat and diploid rice. We show that this mutation detection method is more sensitive than Sanger sequencing and more applicable than PCR/RE method without the requirement for restriction enzyme site. We also demonstrate that this detection method is especially useful for genome editing in wheat, because target sites are often surrounded by single nucleotide polymorphisms. Using this screening method, we were also able to detect foreign DNA‐free tagw2 mutations induced by purified TALEN protein. Finally, we show that partial base editing mutations can also be detected using high‐fidelity SpCas9 variants or FnCpf1. The PCR/RNP method is low‐cost and widely applicable for rapid detection of genome‐edited mutation in plants.
原文链接:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/pbi.12938




