中药丹参基因遗传密码破译
来源:《Molecular Plant》
作者:Haibin Xu等
时间:2016-04-19

近日,中国中医科学院中药研究所陈士林团队和中国科学院植物研究所漆小泉团队联合中国医学科学院药用植物研究所、澳大利亚昆士兰大学、美国田纳西州大学健康科学中心、美国爱荷华州立大学、澳门大学、英国桑格研究院和广药集团等单位,在著名植物学杂志《Molecular Plant》发表丹参全基因组,标志着作为常用中药丹参的遗传密码被破译,为揭示丹参主要药理活性成分丹参酮和丹参酚酸生物合成及其调控的分子机制,促进丹参优良品种选育提供了重要的遗传背景基础。
丹参全基因组解析项目的完成极大促进了丹参生物学研究,已支撑一批高水平研究成果相继完成或发表。陈士林团队与广药集团等企业形成产学研互动,为丹参栽培和质量控制提供理论基础,为创新性药物生产提供新的手段。以上系列工作确立了以基因组为突破口的药用模式植物研究与应用新思路,继灵芝基因组之后再次引发本草基因组效应,创建了以药用模式生物为平台的中药研究新理念。
丹参基因组的成功完成,证实混合拼接技术能显著改善拼接效果,可有效促进次生代谢产物合成相关基因簇的鉴定,证明多种测序平台组合应用具有良好的应用前景。
该文通讯作者是陈士林和漆小泉研究员。陈士林现任中国中医科学院中药研究所所长、世界卫生组织传统医学合作中心主任、教育部长江学者和创新团队发展计划“中药资源学”负责人,首次提出本草基因组的学术方向并开展了大量相关研究工作。(来源:科技日报 杨朝晖)
Analysis of the genome sequence of the medicinal plant Salvia miltiorrhiza
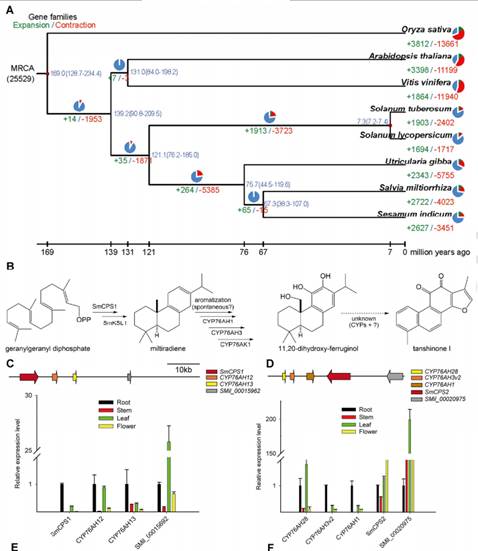
Abstract Here we present a draft assembly of the S. miltiorrhiza genome using long reads from the PacBio RS platform to supplement short Illumina reads, which resulted in significant improvement of the assembly quality. This hybrid approach proved effective for the highly repetitive and complex genome of S. miltiorrhiza, enabling assembly of sufficiently large enough scaffolds for the identification of potential biosynthetic gene clusters. The four CPS/CYP gene clusters revealed here, along with other genes potentially encoding biosynthetic enzymes (e.g., in tashinone biosynthesis - Supplementary Table 9), provide a strong foundation for understanding the biochemical diversity and pharmaceutical qualities of S. miltiorrhiza. Moreover, access to the genome sequence is further expected to enable molecular breeding with this important traditional medicinal herb.
原文链接:http://www.cell.com/molecular-plant/pdf/S1674-2052(16)30005-3.pdf




