研究报道一种药物发现新策略
来源:《化学科学》
作者:杨永亮等
时间:2015-05-11
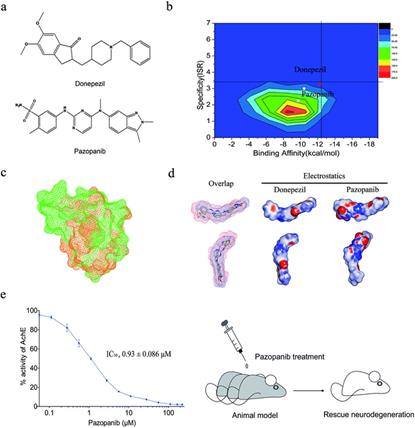
4月29日,大连理工大学生命科学与技术学院杨永亮博士实验室在Chemical Science杂志上在线以全文的形式发表了题为: “Computational discovery and experimental verification of tyrosine kinase inhibitorpazopanib for the reverse of memory and cognitive deficits in rat model neurodegeneration”( 酪氨酸激酶抑制剂帕唑帕尼逆转神经退行性疾病大鼠模型记忆和认知缺陷的计算与实验发现)的文章。该文章报道了一种结构生物信息学、化学生物学、疾病模式动物实验等相结合的药物发现新策略。
乙酰胆碱酯酶是存在于人类神经肌肉接头中的一种酶, 是神经退行性疾病、青光眼等疾病的重要调控靶点。该工作首先大规模分析了美国FDA上市药物及靶点数据库,通过靶点结合口袋三维相似性的比较、药物二维结构相似性的比较、及静电势的相似性比较等结构生物信息学手段,预测了一种用于治疗肾癌的上市药物帕唑帕尼可以靶向结合乙酰胆碱酯酶。通过化学生物学、疾病模式动物实验等手段进一步证实,1/5临床安全剂量的帕唑帕尼(15mg/kg/每天)即可以有效的逆转神经退行性疾病的症状,其效果与已上市的神经系统保护药物Donepezil相当,且人体安全性良好。该项工作为相关的创新药物研发提供了崭新的角度与思路。
该工作得到了自然科学基金委和辽宁省政府的资助,历时约2年完成。该项研究成果已经申请专利《嘧啶胺类化合物在制备乙酰胆碱酯酶抑制剂中的应用》,目前已有多家国内外制药公司联系技术转让。
杨永亮实验室致力于药物发现、生物信息学、化学生物学等领域的综合交叉研究,注重将计算策略与相关实验手段相结合进行重要生物靶标及其活性调控分子的发现与探索。近期,利用设计的亲电性碎片‘垂钓’化合物数据库的虚拟筛选策略,实验室成功的发现了一个马来酰亚胺类小分子NS-0011可以通过共价结合的方式靶向作用于细胞核输出蛋白XPO1结合口袋区的半胱氨酸基团,从而成为小分子共价抑制剂。XPO1蛋白是恶性肿瘤增殖与迁移的关键靶标,目前,通过与厦门大学医学院张杰教授等单位合作,在疾病模式动物上证实了该化合物可以显著的降低胃癌的增生和成瘤,该工作于2015年1月21日已在线发表于Clinical Cancer Research杂志上,化合物NS-0011目前正进行成药性的探索,杨永亮博士为文章的合作通讯作者。以上工作也是该实验室于2013年在J Comput Chem.杂志以封面故事的形式发表研究论文后的一些后继科研成果。
Chemical Science(Chem. Sci.)杂志是英国皇家化学会最新创办的化学领域的旗舰期刊,在创刊之后的短短3年内,该杂志已经加入JACS 和ACIE行列,成为所有化学相关领域中最具影响力的核心期刊之一,并为Nature Index(NI)收录。(来源:科学网 刘万生 龙海波)
Abstract Cognition and memory impairment are hallmarks of the pathological cascade of various neurodegenerative disorders. Herein, we developed a novel computational strategy with two-dimensional virtual screening for not only affinity but also specificity. We integrated the two-dimensional virtual screening with ligand screening for 3D shape, electrostatic similarity and local binding site similarity to find existing drugs that may reduce the signs of cognitive deficits. For the first time, we found that pazopanib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor marketed for cancer treatment, inhibits acetylcholinesterase (AchE) activities at sub-micromolar concentration. We evaluated and compared the effects of intragastrically-administered pazopanib with donepezil, a marketed AchE inhibitor, in cognitive and behavioral assays including the novel object recognition test, Y maze and Morris water maze test. Surprisingly, we found that pazopanib can restore memory loss and cognitive dysfunction to a similar extent as donepezil in a dosage of 15 mg kg−1, only one fifth of the equivalent clinical dosage for cancer treatment. Furthermore, we demonstrated that pazopanib dramatically enhances the hippocampal Ach levels and increases the expression of the synaptic marker SYP. These findings suggest that pazopanib may become a viable treatment option for memory and cognitive deficits with a good safety profile in humans.
原文链接:http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlepdf/2015/SC/C4SC03416C




