不对称的氨基酸α-芳基化修饰是开发新药物的起点
来源:《自然》
作者:Daniel J. Leonard等
时间:2018-11-13
氨基酸是蛋白的构成单元(building block)。对氨基酸进行化学修饰允许科学家们能够开发新的分子,这就为开发抗生素等新的医学药物提供起点。
在一项新的研究中,来自英国布里斯托大学化学学院的研究人员如今开发出一种新的修饰氨基酸的方法:将一个碳原子环连接到氨基酸分子的正中心。相关研究结果发表在2018年10月4日的Nature期刊上,论文标题为“Asymmetric α-arylation of amino acids”。
引入这种碳原子环的不同寻常的化学反应在此之前具有有限的应用,但是这项新的研究表明引入这种新的分子结构特征能够与一系列比之前更加广泛的化学结构兼容。
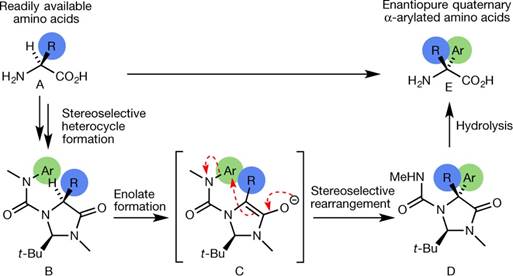
这种化学反应涉及将这个碳原子环从氨基酸的氮原子迁移到它的碳原子上,这是因为氨基酸以两种镜像形式存在,重要的是它在反应产物中保留着对起始镜像结构的记忆。
这种化学反应也很容易大规模进行,这使得合成新的药物分子具有潜在的价值。Jonathan Clayden教授说,“这项研究让我们能够将科学好奇心转化为一种真正实用的构建新型化学构成单元的新方法。它将为科学家们提供一套全新的经过修饰的氨基酸分子,用于产生新的药物或经过修饰的蛋白,从而能够加快对天然的生化系统或疾病治疗的理解。”(来源:生物谷 Bioon.com)
Asymmetric α-arylation of amino acids
Abstract Quaternary amino acids, in which the α-carbon that bears the amino and carboxyl groups also carries two carbon substituents, have an important role as modifiers of peptide conformation and bioactivity and as precursors of medicinally important compounds1,2. In contrast to enantioselective alkylation at this α-carbon, for which there are several methods3,4,5,6,7,8, general enantioselective introduction of an aryl substituent at the α-carbon is synthetically challenging9. Nonetheless, the resultant α-aryl amino acids and their derivatives are valuable precursors to bioactive molecules10,11. Here we describe the synthesis of quaternary α-aryl amino acids from enantiopure amino acid precursors by α-arylation without loss of stereochemical integrity. Our approach relies on the temporary formation of a second stereogenic centre in an N′-arylurea adduct12 of an imidazolidinone derivative6 of the precursor amino acid, and uses readily available enantiopure amino acids both as a precursor and as a source of asymmetry. It avoids the use of valuable transition metals, and enables arylation with electron-rich, electron-poor and heterocyclic substituents. Either enantiomer of the product can be formed from a single amino acid precursor. The method is practical and scalable, and provides the opportunity to produce α-arylated quaternary amino acids in multi-gram quantities.
原文链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0553-9.pdf




