中科院遗传发育所水稻基因组编辑研究取得重要新进展
来源:《分子植物》
作者:李家洋等
时间:2017-07-19
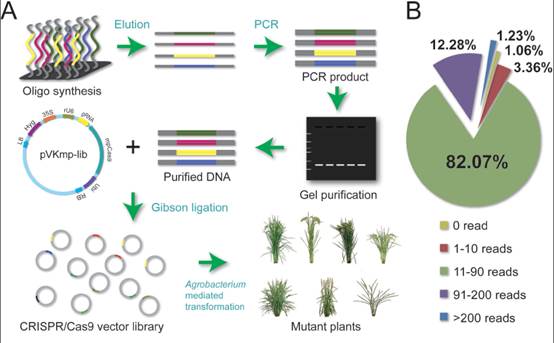
水稻突变体是进行水稻功能基因组学基础研究和水稻分子设计育种的重要材料。常规的水稻突变体来源于自发突变或化学、物理及生物的诱变,具有很大的随机性和局限性,不能满足大规模的水稻功能基因组学研究和水稻分子设计育种的需求。利用高效便捷的CRISPR/Cas9基因组编辑技术和高通量的寡核苷酸芯片合成技术可以大规模地对水稻全基因组进行编辑,实现水稻突变体的高通量构建和功能筛选。该研究通过农杆菌介导的水稻遗传转化法,以水稻中花11作为受体材料,对水稻茎基部和穗部高表达的12802个基因进行高通量的基因组编辑,获得了14000余个独立的T0代株系,并对它们的后代进行了部分表型和基因型分析鉴定。这些研究表明,利用CRISPR/Cas9基因组编辑技术大规模构建水稻突变体库并进行功能筛选是高效便捷获得水稻重要突变体和快速克隆对应基因的有效方法,同时能够为水稻分子设计育种提供重要的供体材料。
该研究成果已于2017年6月21日在Molecular Plant杂志在线发表 (DOI:10.1016/j.molp.2017.06.006),中国科学院遗传与发育生物学研究所李家洋研究组助理研究员孟祥兵和副研究员余泓为该论文的共同第一作者,李家洋研究员和高彩霞研究员为共同通讯作者。该研究得到了国家重点研发计划和国家自然科学基金项目的资助。
此外,李家洋研究组还与中国水稻研究所王克剑研究组合作探索更为高效的水稻CRISPR/Cas9基因组编辑技术,并于6月12日在Plant Biotechnology Journal杂志在线发表了研究论文“Increasing the efficiency of CRISPR-Cas9-VQR precise genome editing in rice”(DOI:10.1111/pbi.12771)。该研究通过优化sgRNA的结构以及使用水稻内源性强启动子来驱动Cas9-VQR变体的表达,显著提高了CRISPR-Cas9-VQR系统在水稻中的基因组编辑效率。水稻所硕士研究生胡熙璕和中科院遗传发育所助理研究员孟祥兵为该论文的共同第一作者,李家洋研究员和王克剑研究员为共同通讯作者。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金、中国农科院科技创新工程经费的资助。(来源:科学网)
Construction of a genome-wide mutant library in rice using CRISPR/Cas9
Abstract We report the construction of a high-throughput CRISPR/Cas9 mutant library in rice, and demonstrate its application to identifying gene functions and its potential use for genetic improvement. We searched the rice genome and identified 1,535,852 target sites located in the exon regions of 52,916 rice genes. To generate loss-of-function mutations efficiently, sgRNA target sites were designed in exons near the beginning of ORFs just downstream of start codons. We chose the first two identified sgRNA target sites in each candidate gene and selected 12,802 genes highly expressed in rice shoot base tissue (rice expression profiles database RED) and 25,604 corresponding sgRNAs to generate a large-scale mutant library. The sequence data showed that 25,265 of the 25,604 sgRNAs were represented by at least one read (98.7%), and these 25,265 sgRNAs covered 12,786 genes (99.9%). The majority (82.1%) of the sgRNAs had 11-90 reads, pointing to very high coverage and evenness of the sgRNA library. In summary,we have constructed a large-scale CRISPR/Cas9 mutant library in rice that is of high quality, with good coverage and uniform distribution. Our study demonstrates that CRISPR/Cas9-based screening is a robust method for systematically identifying both genes and mutant phenotypes in rice. The mutant library developed here will be of great value for the study of gene functions in rice and for crop improvement.
原文链接:http://www.cell.com/molecular-plant/pdf/S1674-2052(17)30172-7.pdf?_returnURL=http%3A%2F%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%2Fretrieve%2Fpii%2FS1674205217301727%3Fshowall%3Dtrue




