与青蒿素齐名的雷公藤红素或可治疗肥胖
来源:Molecular Cell
作者:张晓坤等
时间:2017-04-18
记者从厦门大学获悉,该校药学院张晓坤教授课题组的一项最新成果在国际一流学术期刊《细胞》杂志子刊《分子细胞》发表,揭示了从传统药用植物雷公藤中分离提取的雷公藤红素调控代谢的重要作用靶点和机制,发现肥胖的潜在治疗方法。
雷公藤红素与青蒿素齐名,被《细胞》杂志列为最有可能被开发成为现代药物的5种传统天然药用化合物之一。最近发现的雷公藤红素的超级减肥作用更使这一传统中药成分风靡世界。然而雷公藤红素具体的作用靶点不清、分子机制不明, 一直阻碍了将其开发成为现代药物。
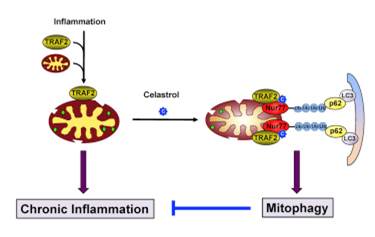
而张晓坤教授课题组最新发现,雷公藤红素能够结合于细胞核中的孤儿核受体Nur77,诱导产生特定的机理作用,清除损伤的线粒体,从而抑制炎症及肥胖等相关疾病。实验结果明显看出,雷公藤红素有效地抑制了喂食高脂肪饮食的小鼠体重增加。
这一结果确定了雷公藤红素作用的特异性靶点及新型的分子作用机理,突破了天然产物转化为现代药物过程中的重大难题,为开发雷公藤红素的药用价值奠定了强而有力的理论基础,有利于推动炎症性疾病及肥胖治疗药物的开发。在调节代谢中起重要作用的孤儿核受体Nur77,将是治疗肥胖的潜在药物靶点。
据了解,张晓坤教授课题组下一步的研究将深入探索雷公藤红素如何作用于线粒体而调控新陈代谢。研究发现雷公藤红素能使细胞对瘦素(一种抑制食欲、抑制脂肪细胞合成的激素)更敏感,因此课题组计划在大脑的食欲调控中心寻找孤儿核受体Nur77与瘦素信号的联系。(来源:科技日报 张建琛 翁舒昕)
Celastrol-Induced Nur77 Interaction with TRAF2 Alleviates Inflammation by Promoting Mitochondrial Ubiquitination and Autophagy
Abstract Mitochondria play an integral role in cell death, autophagy, immunity, and inflammation. We previously showed that Nur77, an orphan nuclear receptor, induces apoptosis by targeting mitochondria. Here, we report that celastrol, a potent anti-inflammatory pentacyclic triterpene, binds Nur77 to inhibit inflammation and induce autophagy in a Nur77-dependent manner. Celastrol promotes Nur77 translocation from the nucleus to mitochondria, where it interacts with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2), a scaffold protein and E3 ubiquitin ligase important for inflammatory signaling. The interaction is mediated by an LxxLL motif in TRAF2 and results not only in the inhibition of TRAF2 ubiquitination but also in Lys63-linked Nur77 ubiquitination. Under inflammatory conditions, ubiquitinated Nur77 resides at mitochondria, rendering them sensitive to autophagy, an event involving Nur77 interaction with p62/SQSTM1. Together, our results identify Nur77 as a critical intracellular target for celastrol and unravel a mechanism of Nur77-dependent clearance of inflamed mitochondria to alleviate inflammation.
原文链接:http://www.cell.com/molecular-cell/pdf/S1097-2765(17)30198-3.pdf




