科学家发现减肥植物的有效成分及机制
来源:《美国科学院院刊》
作者:谢欣
时间:2014-11-04
中国科学院上海药物研究所谢欣课题组与中国科学院上海有机化学研究所俞飚课题组合作,发现了减肥植物蝴蝶亚仙人掌的有效成分及减肥机制。研究论文于9月22日在线发表于《美国科学院院刊》上。
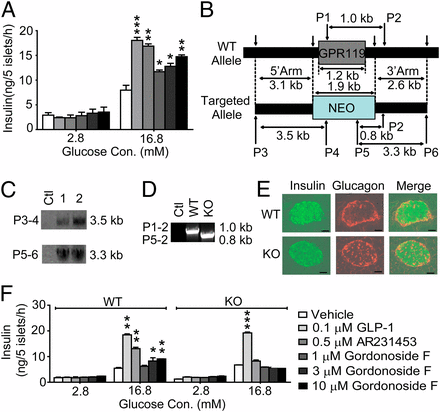
有文献报道蝴蝶亚仙人掌中的一个化合物P57是其抑制食欲的主要活性成分,但其作用机制并不清楚。研究团队通过大量化合物筛选发现一个提取自蝴蝶亚仙人掌的化合物Gordonoside F,而不是P57,可以特异性激活与代谢密切相关的G蛋白偶联受体GPR119。Gordonoside F通过激活GPR119刺激胰高血糖素样肽-1(GLP-1)和胰岛素的分泌,并抑制小鼠食欲。
在GPR119敲除小鼠中,其药效消失。更有意思的是,蝴蝶亚仙人掌的粗提物也是部分通过激活GPR119来抑制食欲的。这类新型GPR119激动剂的发现为抗肥胖药物的开发奠定良好基础。该研究工作得到新药创制重大专项、国家自然科学基金、“973”及上海市科委项目的支持。 (来源:中国科学报 红枫)
Molecular matchmaking between the popular weight-loss herb Hoodia gordonii and GPR119, a potential drug target for metabolic disorder
Abstract African cactiform Hoodia gordonii (Asclepiadaceae) has been used for thousands of years by Xhomani Bushmen as an anorexant during hunting trips and has been proposed as a new agent for the management of body weight. However, its in vivo targets and molecular mechanisms remain elusive. GPR119, a G protein-coupled receptor highly expressed in pancreatic β cells and intestinal L cells, has been demonstrated to facilitate glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) and represents a novel and attractive target for the therapy of metabolic disorders. Here, we disclose that Gordonoside F (a steroid glycoside isolated from H. gordonii), but not the widely known P57, activates specifically GPR119. Successful synthesis of Gordonoside F facilitates further characterization of this compound. Gordonoside F promotes GSIS both in vitro and in vivo and reduces food intake in mice. These effects are mediated by GPR119 because GPR119 knockout prevents the therapeutic effects of Gordonoside F. Interestingly, the appetite-suppressing effect of Hoodia extract was also partially blocked by GPR119 knockout. Our results demonstrate for the first time, to our knowledge, that GPR119 is a direct target and one of the major mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effect of the popular “weight loss” herb H. gordonii. Given the long history of safe application of this herb in weight control, it is foreseeable that the novel scaffold of Gordonoside F provides a promising opportunity to develop new drugs in treating metabolic diseases.
原文链接:http://www.pnas.org/content/111/40/14571.full.pdf+html




