大麻成分有望治疗阿尔茨海默病
来源:《Journal of Alzheimer's Disease》
作者:Chuanhai Cao
时间:2014-09-24
近日,一项发表在《Journal of Alzheimer's Disease》杂志上的研究中,来自南佛罗里达大学的神经科学家们发现,一种在大麻中含量极低的化合物δ-9-四氢大麻酚(THC)有望减缓或者阻止阿尔茨海默病的发展。
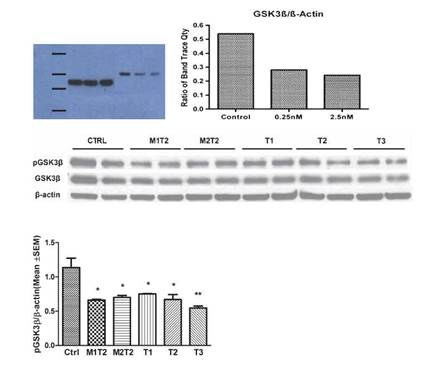
研究人员发现,极低剂量的THC就能够减少β淀粉样蛋白的产生,并防止这种蛋白的异常积累。β淀粉样蛋白通常以可溶性的形式存在于大部分衰老的大脑中,它的异常积累通常被认为是记忆丧失类的疾病最早期的病理特征之一。低浓度的THC还能够选择性的增强线粒体的功能;线粒体对一个健康的大脑起到能量供给,信号传递的作用。
该研究的第一作者Chuanhai Cao博士说:”THC为人所知的是它的抗氧化性和神经保护作用。该研究首次证明了THC能够通过降低β淀粉样蛋白的水平,抑制它的积累并增强线粒体的功能,从而影响阿尔茨海默病的病理。THC是一种天然的淀粉样蛋白抑制剂,有望在未来对阿尔茨海默病的治疗发挥作用。“
此外,参与研究的Neel Nabar博士称,医用大麻的争论从未停止过,相关的政策环境也在不断变化。他说:”虽然我们的研究表示THC可能具有治疗阿尔茨海默病的价值,但是这并不表示我们提倡人们用非法的药物来治疗疾病。我们可以基于这项研究开发其它治疗阿尔茨海默病的安全合法的化合物。”
Cao博士的实验室目前正在研究一种药物组合(包括THC、咖啡因和一些其它天然化合物)对阿尔茨海默氏症细胞模型的作用,并将进一步进行转基因小鼠试验。Cao博士还表示:“对任何药物而言,剂量和靶标都是至关重要的,所以认真监测药物在血液和系统中的含量对治疗过程非常必要,尤其是像从大麻中提出的THC这类化合物。”
关于THC
δ-9-四氢大麻酚(THC)是是大麻中的主要精神活性物质,最早由以色列雷霍沃特魏茨曼科学研究所的三名研究人员在1964年分离出来。历史上大麻曾被用作麻醉剂,其麻醉成分就是四氢大麻酚,后被停止使用。此前有研究称,合成的THC可能具有抵抗HIV-1病毒感染的作用。( 来源:生物探索)
The Potential Therapeutic Effects of THC on Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract The purpose of this study was to investigate the potential therapeutic qualities of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) with respect to slowing or halting the hallmark characteristics of Alzheimer's disease. N2a-variant amyloid-β protein precursor (AβPP) cells were incubated with THC and assayed for amyloid-β (Aβ) levels at the 6-, 24-, and 48-hour time marks. THC was also tested for synergy with caffeine, in respect to the reduction of the Aβ level in N2a/AβPPswe cells. THC was also tested to determine if multiple treatments were beneficial. The MTT assay was performed to test the toxicity of THC. Thioflavin T assays and western blots were performed to test the direct anti-Aβ aggregation significance of THC. Lastly, THC was tested to determine its effects on glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) and related signaling pathways. From the results, we have discovered THC to be effective at lowering Aβ levels in N2a/AβPPswe cells at extremely low concentrations in a dose-dependent manner. However, no additive effect was found by combining caffeine and THC together. We did discover that THC directly interacts with Aβ peptide, thereby inhibiting aggregation. Furthermore, THC was effective at lowering both total GSK-3β levels and phosphorylated GSK-3β in a dose-dependent manner at low concentrations. At the treatment concentrations, no toxicity was observed and the CB1 receptor was not significantly upregulated. Additionally, low doses of THC can enhance mitochondria function and does not inhibit melatonin's enhancement of mitochondria function. These sets of data strongly suggest that THC could be a potential therapeutic treatment option for Alzheimer's disease through multiple functions and pathways.
原文链接:http://iospress.metapress.com/content/8421pvx80144t354/fulltext.pdf




